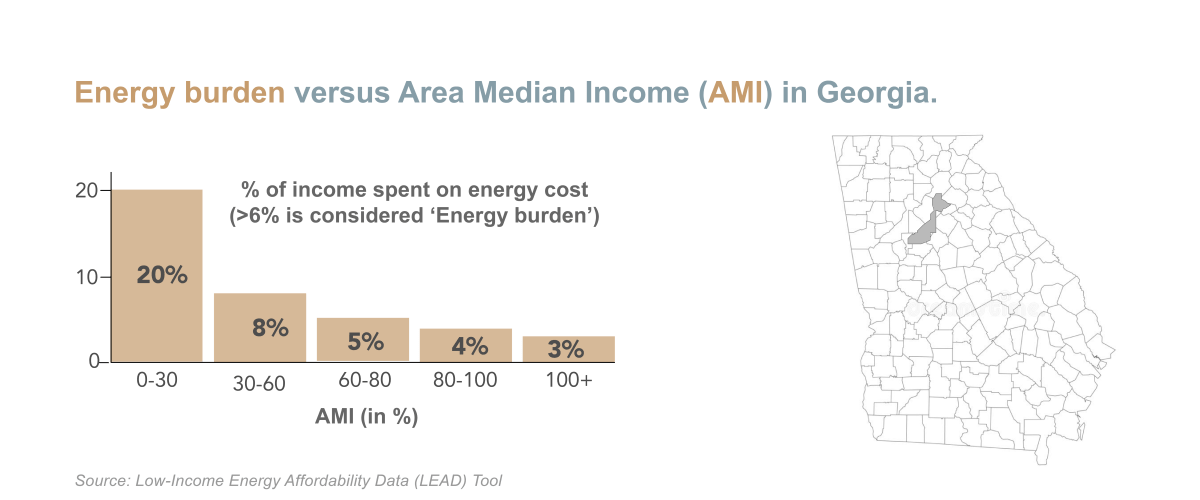Get Introduced
Click on these icons to learn more about your home’s context.
Atlanta’s Climate Overview
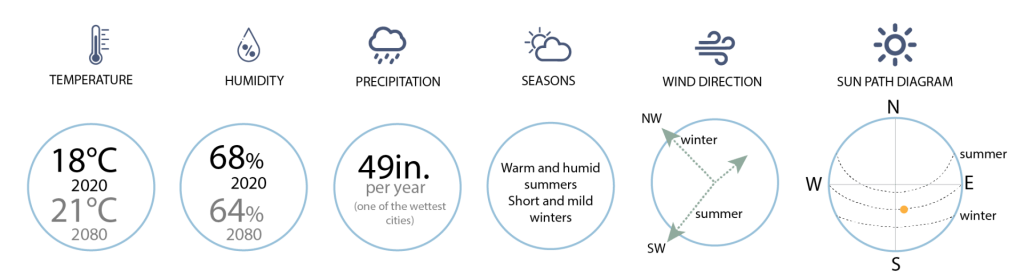
This trend is expected to change with increasing winter temperatures
Check your home’s orientation to the sun
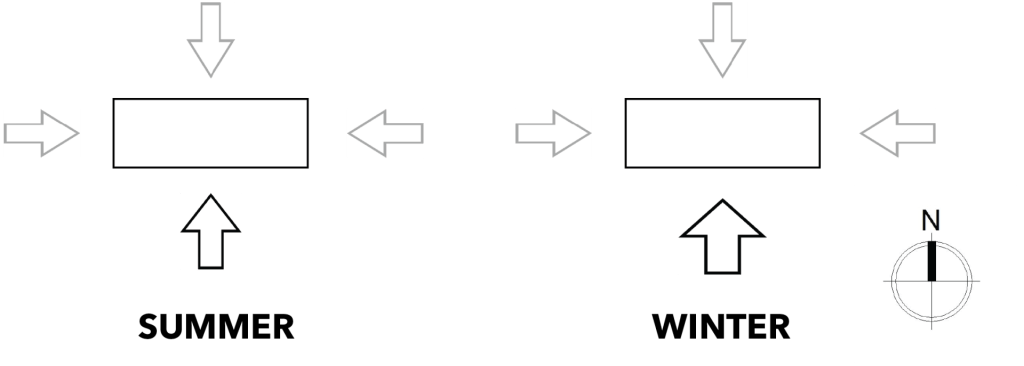
The glazing treatment, window insulation, window shading, and ventilation strategies depend on the orientation of your house. So make sure to check your home’s orientation and then plan strategies to take advantage of the prevailing climate and its benefits
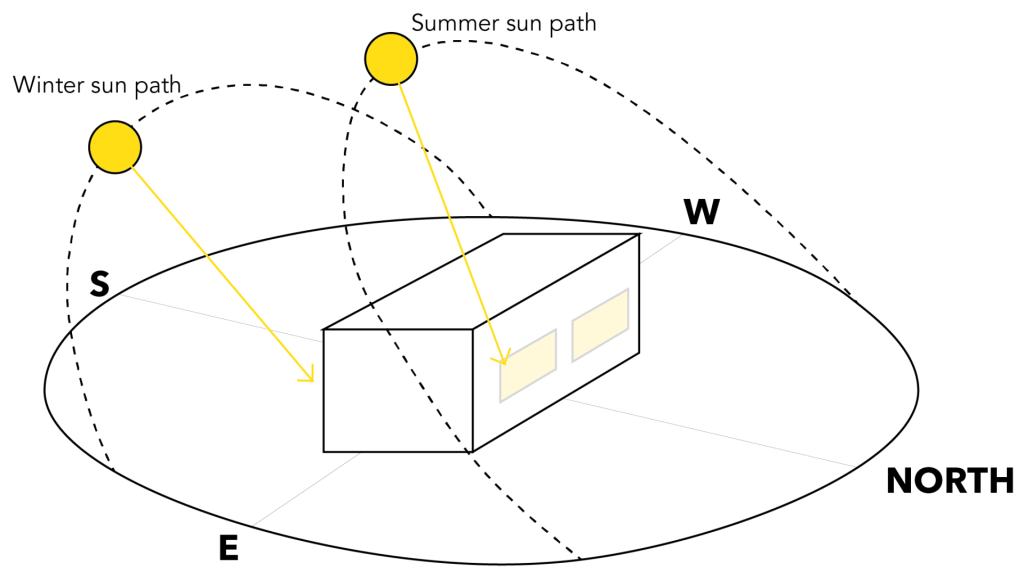
Solar radiation experienced during summers and winters is different along the four axes. In winter, the sun’s path is at a lower angle, south to E-W. In summer, the sun’s path is at a high angle sun, north to E-W axis. As a result, the East and West façades receive strong solar radiation at low angles throughout the year.
Utility Bills
Power Bill 
Use this calculator from Georgia Public Service Commission
(GPSC) to calculate your power bill based on actual usage.
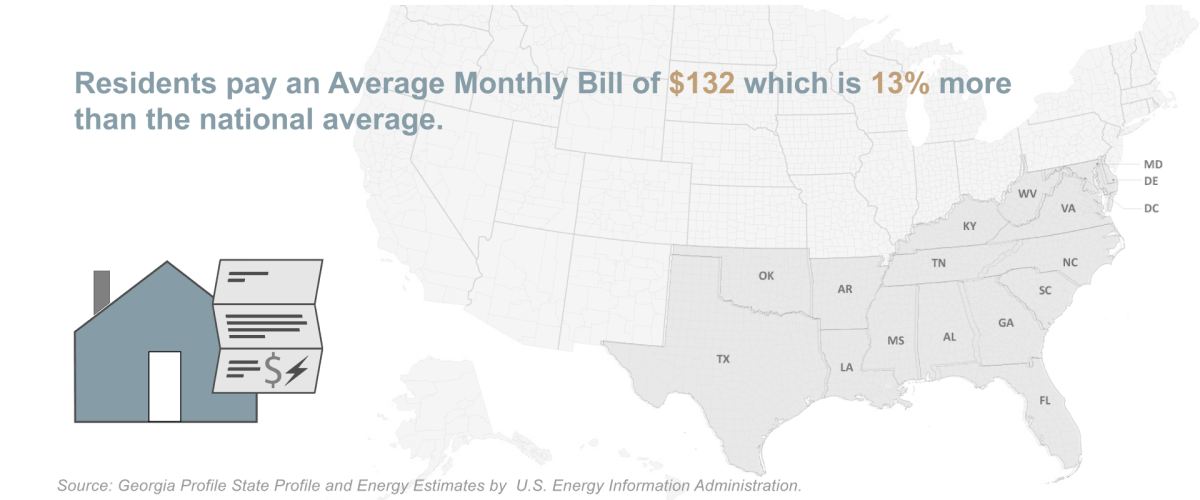
According to US Energy Information Administration (EIA),
the average residential monthly use in Georgia is 1080
KWh, which results in monthly costs of $130 per home. If your power bills are significantly higher than this value, you might have to inspect the house professionally and follow recommendations for reducing energy usage.
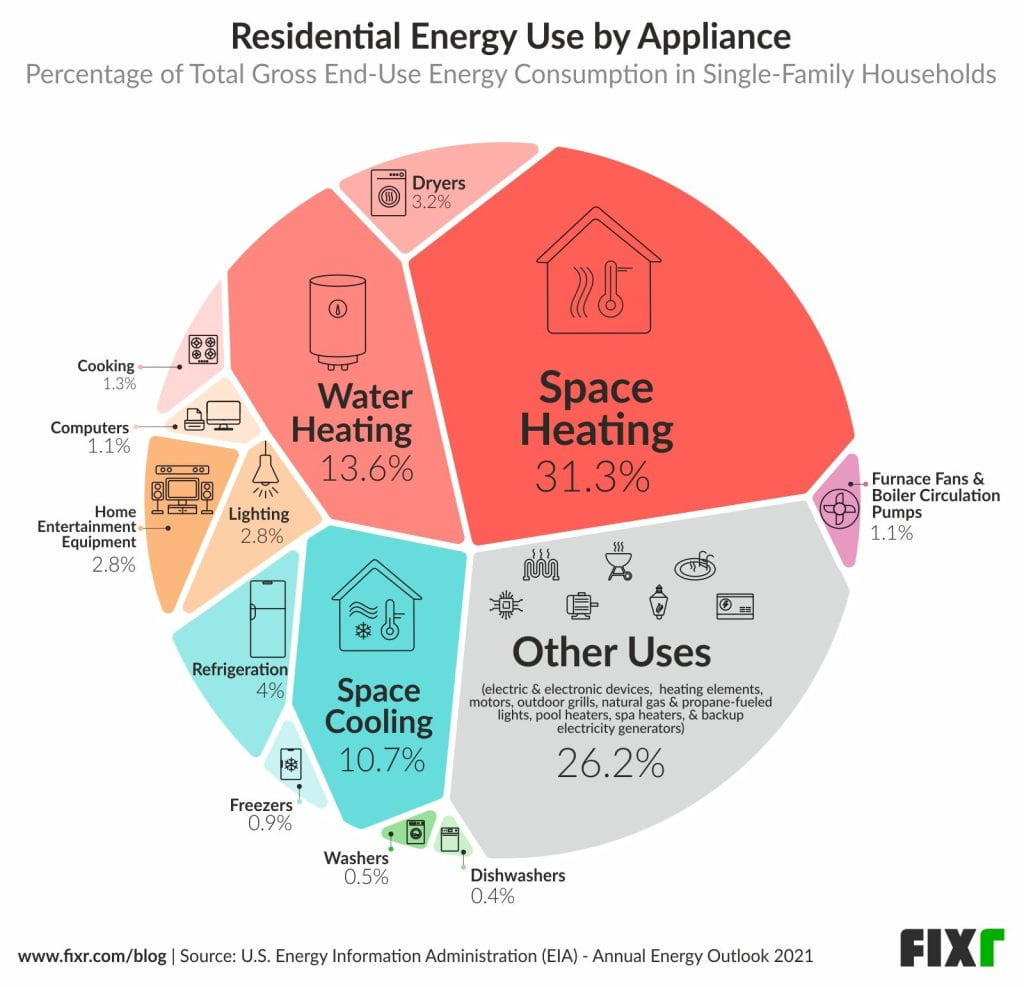
Learn more about your Power Bill here
Water Bill 
Do you know that in Georgia residents pay more for sewer rates than water rates?
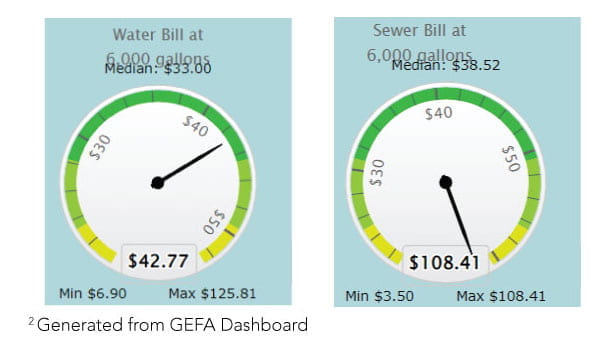
Use this estimator to calculate your monthly utility bills by the 2022 Environmental Finance Center at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
The EPA estimates that an average household uses 100 gallons of water per person daily. However, in Georgia, residents pay more for sewer than water. This can cost up to $42 ($5.52 per 100 cubic feet) as water costs and $109 for sewer bills, totaling $151 for the family. Click here to learn more about Fulton county’s rate schedule.
Learn more about your Water Bill here
Natural Gas Bill 

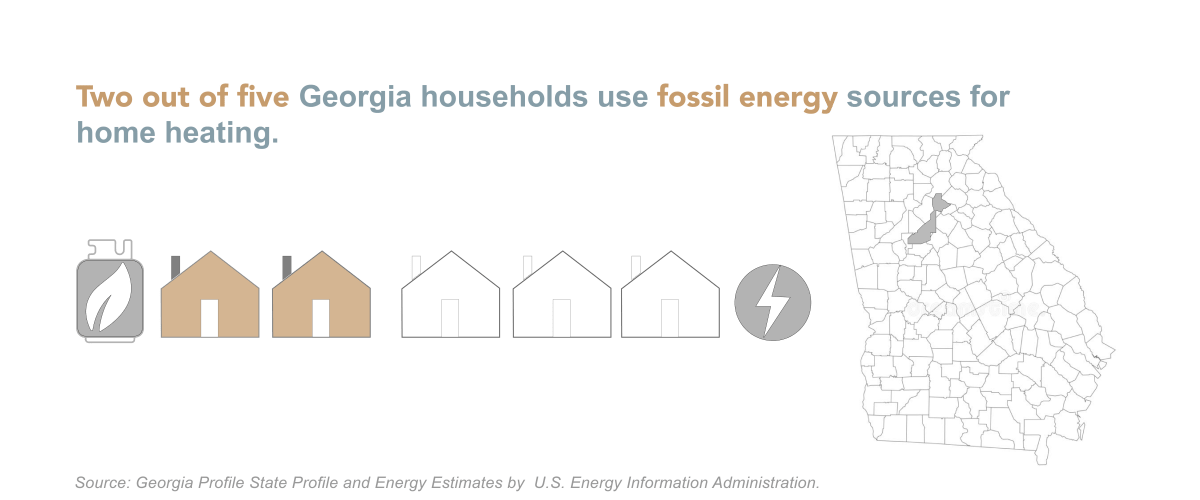
48% of Georgia homes use natural gas for heating, and 48% use electricity for heating.
If you are paying significantly more than $160 (with heating
use), then you might have to call for a professional inspection of your devices and switch to newer systems that are more efficient.
Learn more about your Natural Gas Bill here
Weatherization
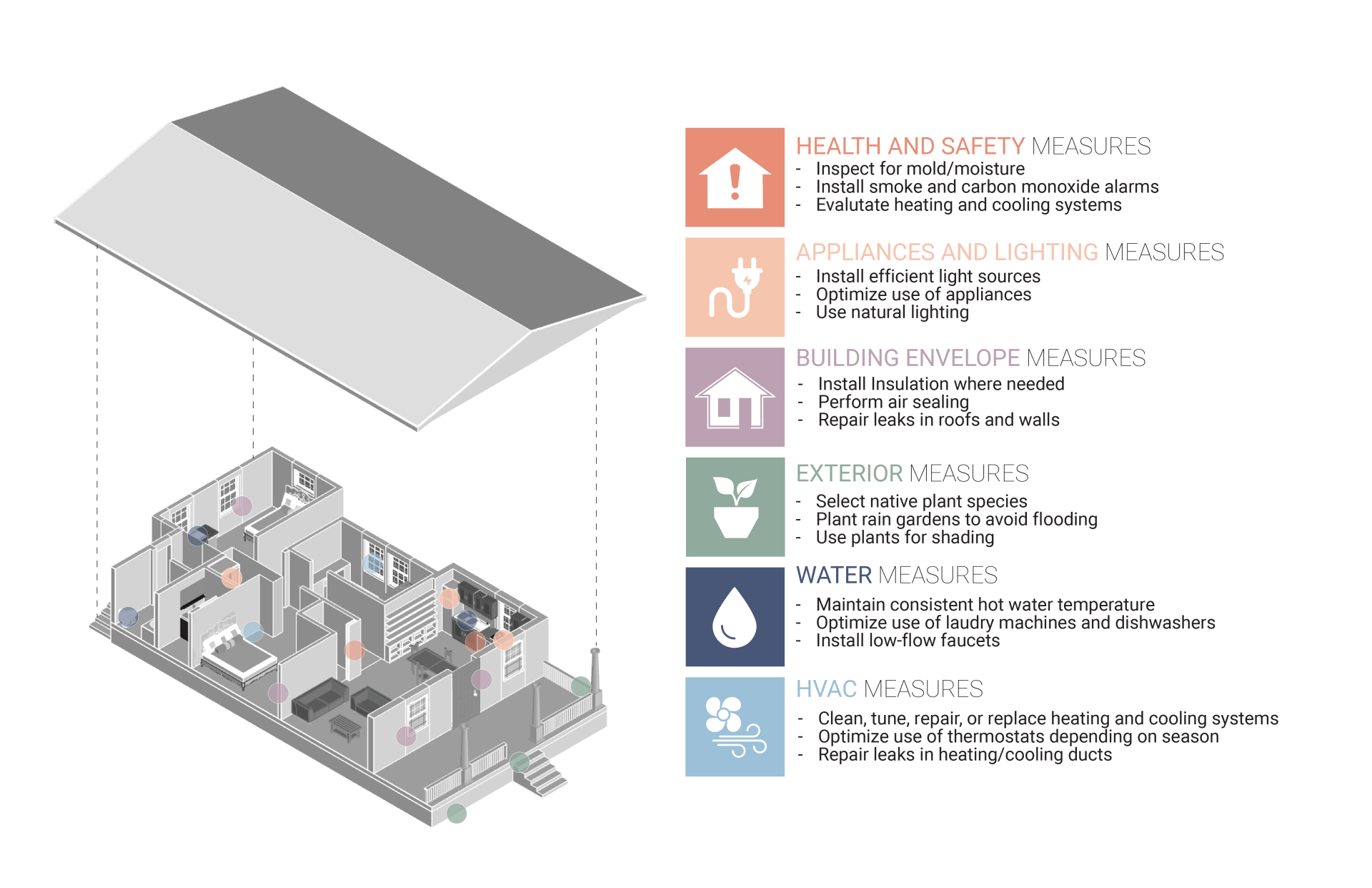
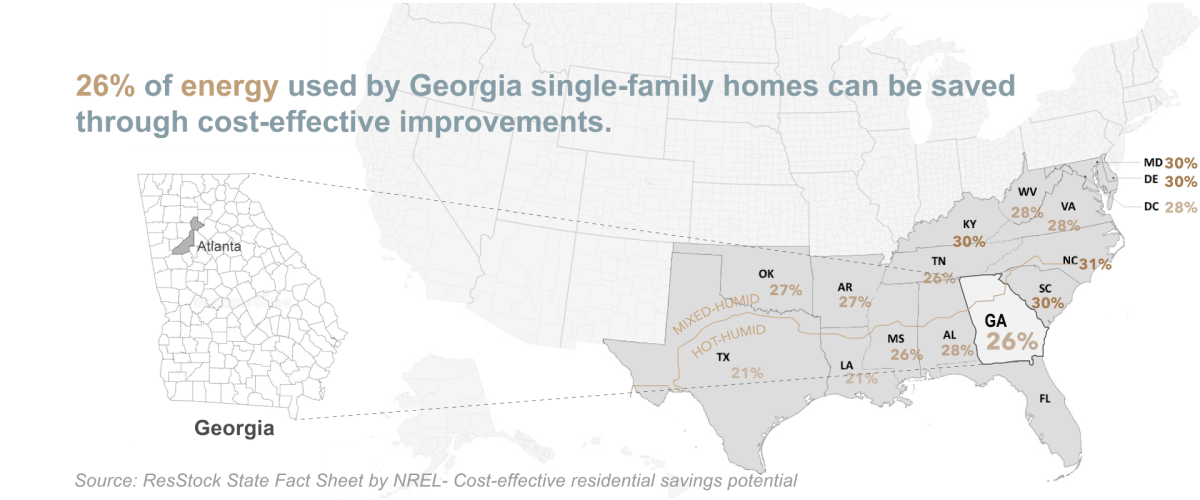
Weatherization is a systemic process to make a home more comfortable, reduce energy waste and lower its carbon footprint. Weatherization can save the homeowner 20-30% on utility bills or $283 per year, with even higher savings reported in some parts of the country.
Data
This project is made possible with the generous support of New Venture Fund/Public Interest Technology-University Network, Georgia Tech College of Design and the School of Architecture.